Overview

Carrier Ethernet has truly become the global service. Delivering services across multiple regions and operators and interconnecting to out-of-franchise Enterprise customer locations and cell towers is a business necessity that requires wholesale arrangements between service providers.
A Heavy Reading five-year market forecast projects wholesale Ethernet revenues to grow by over 30% a year, and concludes that “Wholesale Ethernet is finally emerging as a major, thriving U.S. market.” This market growth is driven by demand for business services and mobile backhaul that connect customers regionally, nationally and globally across multiple operator networks.
The Wholesale Interconnect Challenge
The challenge with wholesale services is the complex and time-consuming process of interconnecting the wide variety of Carrier Ethernet services. Aligning the different SLAs and the Class of Service (CoS) between Service Providers at the Ethernet Network to Network Interconnect (ENNI) can take weeks and even months of negotiation to create a single end-to-end service.
Carrier Ethernet 2.0 has addressed this challenge with the MEF 33 E-Access standard that simplifies the wholesale service interconnection.E-Access has simplified wholesale Ethernet to be as easy as deploying T1 services by reducing deployment costs and shortening time to revenue. E-Access provides several benefits to retail and wholesale service providers. Wholesale Ethernet access providers can generate revenue selling existing network footprint as Carrier Ethernet wholesale E-Access service. Retail Ethernet service providers can reduce the time and cost associated with reaching remote end-user locations, and minimize the number of custom interconnect agreements with Access Providers.
The Off-Net Demarcation Challenge
Intelligent Ethernet demarcation is required for traffic management, performance monitoring and fault management. The challenge is how to deploy and maintain Network Interface Devices out-of-franchise where the Service Provider has no facilities to install and maintain the out-of-franchise NID.
Providing demarcation for wholesale Ethernet services has resulted in multiple NIDs at the off-net demarcation point. The retail Service Provider needs to deploy a NID for the end-to-end customer SLA, and the Access Provider needs to deploy a NID for the wholesale service SLA. Two NIDs, and sometimes three or four NIDs, are deployed at the remote customer premises. This multi-NID scenario creates several challenges: there are now more points of failure on the service, multiple NIDs can increase delay, and which NID is actually providing the UNI?
The iConverter SFP-NID® solves this challenge by providing SLA assurance for the retail service provider in a compact SFP that can be installed in the wholesale access provider’s NID. This enables the Service Provider to monitor end-to-end service and without having to deploy and power another standalone NID device at the out-of-franchise customer location.
Wholesale Ethernet Demarcation Products
Wholesale Carrier Ethernet Demarcation Products
iConverter® Carrier Ethernet 2.0 Network Interface Devices
![]()
iConverter NIDs provide MEF Carrier Ethernet 2.0 Certified demarcation and support MEF 33 E-Access for wholesale business services and cloud services. These state-of-the-art NIDs enable business services across multiple service provider networks with advanced service assurance, and reduce operating costs with automated service provisioning and testing.
Wholesale Ethernet Application
Wholesale Carrier Ethernet Service Demarcation
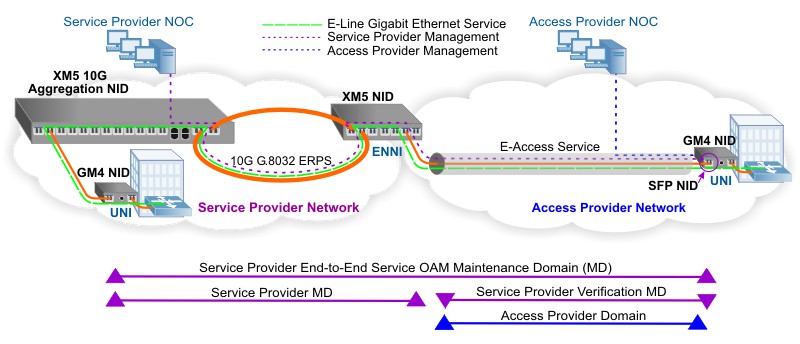
In this application diagram, a Service Provider is delivering a Carrier Ethernet 2.0 E-Line (point-to-point) service to an out-of-franchise (off-net) subscriber and contracts an MEF 33 E-Access service with a regional operator.
The Service Provider deploys iConverter 10G and Gigabit Network Interface Devices (NIDs) for demarcation and aggregation of the business services, and to provide crucial traffic management and performance assurance functions throughout the life cycle of the Carrier Ethernet service.
The Service Provider metro network consists of a 10G resilient ring with ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS). An iConverter XM5 Demarcation and Aggregation NID is deployed at a hub location for connectivity to the 10G G.8032 ring and to provide Gigabit fiber access links. An iConverter GM4 NID provides Carrier Ethernet 2.0 demarcation at the subscriber premises User to Network Interface (UNI).
An iConverter XM5 NID is deployed at a hub location on the 10G ring to provide the Ethernet Network-to-Network Interface (ENNI) between the Service Provider network and the Access Provider network. The Access Provider provides an E-Access Service as part of the MEF 33 E-Access service that connects the ENNI to the UNI at the out-of-franchise customer location. The Access Provider has also deployed an iConverter GM4 NID for demarcation and UNI at the out-of-franchise customer location. The Access Provider installed an iConverter SFP-NID supplied by the Service Provider in the GM4 NID.
The Access Provider can monitor the service from the ENNI to UNI by accessing the iConverter GM4 NID.
The Service Provider can monitor the end-to-end service across the Service Provider metro network, and to the out-of-franchise UNI with the SFP-NID.
The iConverter NIDs on the metro network and customer premises locations provide traffic management for the subscriber traffic across the network. The advanced Traffic Management features enable the Service Provider to offer MEF-certified Carrier Ethernet 2.0 services with Multiple Classes of Service (Multi-CoS), granular rate-limiting, and 802.1ad Provider Bridge VLAN stacking (Q-in-Q) for service multiplexing. GM4 NIDs filter the subscriber traffic, assign the traffic to different Classes of Services, enforce rate-limiting for each CoS, and forward the allowed traffic to the other subscriber locations. Support for per-flow service mapping, traffic policing and shaping transports nearly any type of subscriber traffic as an EVC or CoS flow. In a multi-point E-LAN service, the NIDs also manage traffic delivered to each customer location, monitoring and enforcing the total delivered utilization rate (for billing purposes).
Service activation and testing tools include Zero-Touch Provisioning, and Y.1564 and 2544 test heads, which allow the NIDs to perform tests with synthetic subscriber traffic, and eliminates the need for service personnel and test equipment at the customer premises. Service testing ensures proper service provisioning, validates the Service Level Agreement (SLA) parameters, and helps troubleshoot any service issues. These features shorten time to market and reduce operating costs by simplifying service provisioning and testing.
During operation, the iConverter NIDs constantly communicate with each other, ensuring the service paths between the subscriber locations are uninterrupted. Advanced fault management features include support for IEEE 802.1ag Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) for proactive fault monitoring and isolation, and ITU-T G.8032 Ethernet Ring Protection Switching (ERPS) for resilient rings with sub-50ms failover.
iConverter NIDs provide comprehensive support of the ITU-T Y.1731 Performance Monitoring standard, ensuring the delay, delay variation, loss and availability of the service are meeting the SLA. Support for third-party SLA Portals enable customers access to performance monitoring metrics through the Service Provider’s existing OSS/BSS.










